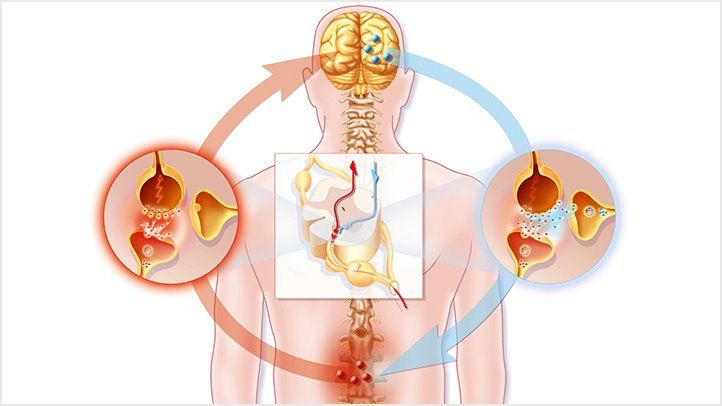
What is Neuropathic pain actully is:
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain that results from damage or disease affecting the somatosensory nervous system.
It is often described as a burning, shooting, or stabbing sensation, and can occur in various parts of the body, such as the hands and feet.
Causes of neuropathic pain include diabetes, injury, infection, and certain medications. It can be difficult to treat and may require a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms.
Sighn of Neuropathic pain:
Signs and symptoms of neuropathic pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and the location of the affected nerves. Some common signs and symptoms include:
-Burning, shooting, or stabbing pain that may be constant or intermittent
-Numbness, tingling, or pins and needles sensations in the affected area
-Sensitivity to touch or temperature changes
-Weakness or muscle wasting in the affected area
-Loss of reflexes
-Difficulty sleeping due to pain
-Depression or anxiety
-Changes in skin color or texture in the affected area
It’s worth noting that not all patients with neuropathic pain will experience all of these symptoms and some may have more unusual symptoms.
A proper diagnosis and treatment plan can be made by a healthcare professional after a thorough examination and assessment of symptoms.
Treatment of Neuropathic pain:
Treatment of neuropathic pain can be challenging, as the underlying cause of the pain may not always be clear and different treatments may be effective for different patients. A combination of treatments is often needed to manage symptoms.
Treatment options for neuropathic pain include:
Medications:
Aspadol 100mg and Aspadol 200mg opioids can be used to reduce neuropathic pain.
Physical therapy: Exercises, massage, and other physical therapies can help to reduce pain and improve function.
Lifestyle changes:
Maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption can help to manage neuropathic pain.
Surgery:
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat the underlying cause of neuropathic pain.
Behavioral therapy:
Cognitive behavioral therapy and other psychological therapies can help patients better cope with the pain and improve their quality of life.
It’s worth noting that treatment plans should be tailored to the individual patient, taking into account their specific symptoms, causes, and other health conditions. A healthcare professional such as a pain specialist or neurologist can help develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Precaution for Neuropathic pain:
Precautions to prevent or manage neuropathic pain may include:
Monitoring and managing underlying medical conditions:
For example, controlling blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes can help to prevent neuropathic pain.
Properly managing medications:
Some medications can cause neuropathic pain as a side effect, so it’s important to use them as directed and to inform the healthcare provider if any new symptoms occur.
Avoiding injury:
Taking steps to prevent injuries, such as wearing appropriate footwear and using handrails when climbing stairs, can help to prevent neuropathic pain from developing.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle:
Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption can help to prevent neuropathic pain from developing.
Good sleep hygiene:
Having a consistent sleep schedule, comfortable mattress and pillows, avoiding caffeine and screens before bedtime can help prevent chronic pain.
Monitoring any changes in symptoms:
Keep a diary of pain symptoms, noting down the intensity, duration, location, and triggers of the pain. This will help to identify patterns and inform the healthcare provider about the progress.
It’s important to note that not all neuropathic pain is preventable, and some people may develop neuropathic pain despite taking precautions. If you suspect that you have neuropathic pain, it is best to see a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Is Neuropathic pain long term pain?
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain, which means that it lasts for a long time, often for months or even years. In some cases, it may be a lifelong condition.
The duration of neuropathic pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of treatment. Some causes of neuropathic pain, such as diabetes, can be managed with proper treatment, which can help to reduce or eliminate the pain.
Other causes, such as nerve injury, may result in permanent nerve damage and chronic pain.
It’s important to note that chronic pain can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life and can lead to depression, anxiety and other physical and mental health issues.
A proper diagnosis and treatment plan can be made by a healthcare professional after a thorough examination and assessment of symptoms. This can help to manage the pain and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Can Neuropathic pain be reversed?
In some cases, neuropathic pain can be reversed or eliminated with proper treatment. The success of treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the neuropathic pain.
If the neuropathic pain is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes, treating the condition can help to reduce or eliminate the pain. For example, controlling blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes can help to prevent neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy.
If the neuropathic pain is caused by nerve damage, treatment options include medications, physical therapy and surgery to treat the underlying condition, which in some cases can lead to a reduction in pain or even complete resolution of the pain.
However, in some cases, neuropathic pain may not be reversible, particularly if the nerve damage is permanent. In these cases, the goal of treatment is to manage the pain and improve the patient’s quality of life.
It’s important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, as the best approach will depend on the underlying cause and the individual patient’s condition.